Thyroid Surgery
All head and neck diseases
Head and neck diseases encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the structures within this region, including the skin, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, and organs such as the mouth, throat, nose, and sinuses. These diseases can be congenital, infectious, inflammatory, or neoplastic (tumors).
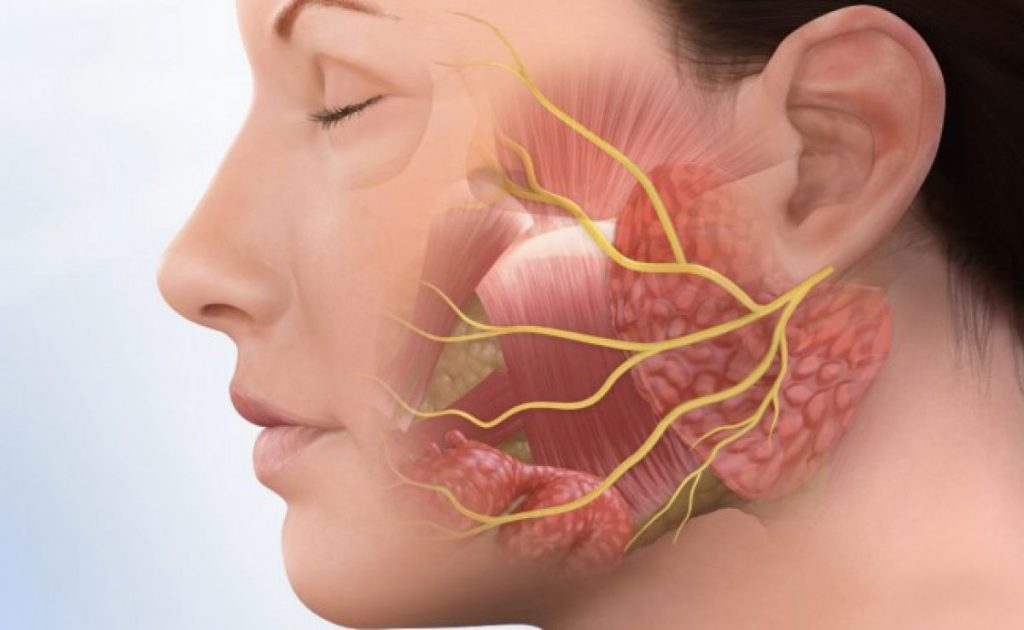
Parotid diseases and surgeries
The parotid glands are the largest of the salivary glands, located in front of and just below each ear. They are responsible for producing saliva, which aids in digestion, keeps the mouth moist, and helps control bacteria in the mouth. The parotid gland has a superficial part that is located outside the mandible and a deep part that extends into the oropharyngeal region.
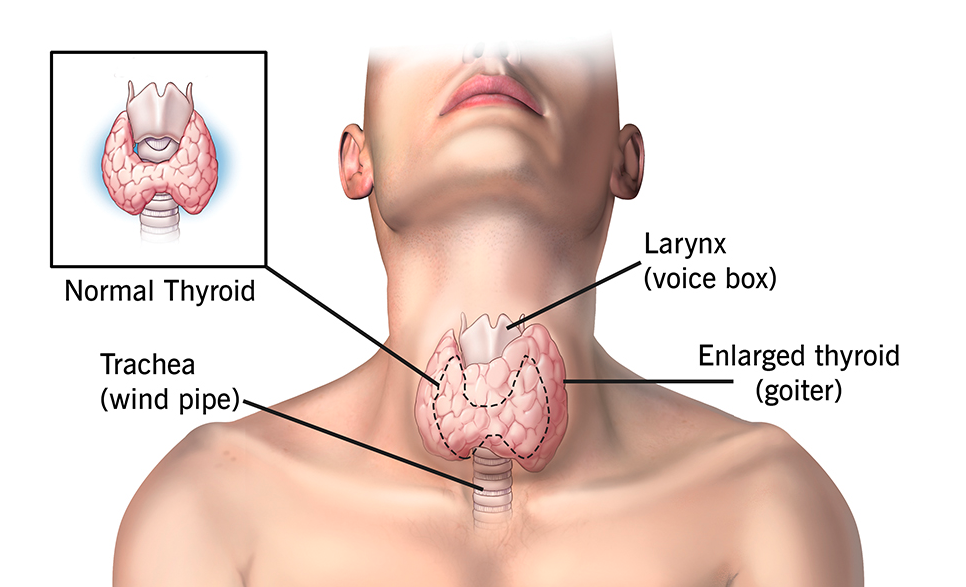
Thyroid diseases and surgeries
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple (thyroid cartilage). It consists of two lobes connected by a narrow band of tissue called the isthmus. The primary function of the thyroid gland is to produce hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development throughout the body.
Thyroglossal diseases
The thyroglossal duct is a structure that forms during embryonic development and normally involutes as the thyroid gland descends to its final position in the neck. It typically extends from the foramen cecum (at the base of the tongue) to the thyroid gland location in the neck.
Cervical lymphadenopathy
Cervical lymphadenopathy refers to the enlargement or swelling of lymph nodes in the neck region. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that play a crucial role in the body’s immune system by filtering lymphatic fluid and trapping pathogens or abnormal cells, such as cancer cells. When lymph nodes in the neck become enlarged, it often indicates an underlying inflammatory condition, infection, or, less commonly, a malignancy.